Today’s digital landscape is constantly changing, and one of the currently fastest growing technologies is known as deepfake technology. Deepfakes have their roots in artificial intelligence and have seen an explosion in popularity as AI technology has been fine-tuned over the years and continues to evolve. But what is deepfake technology, and what is its impact on businesses?
Deepfakes Defined
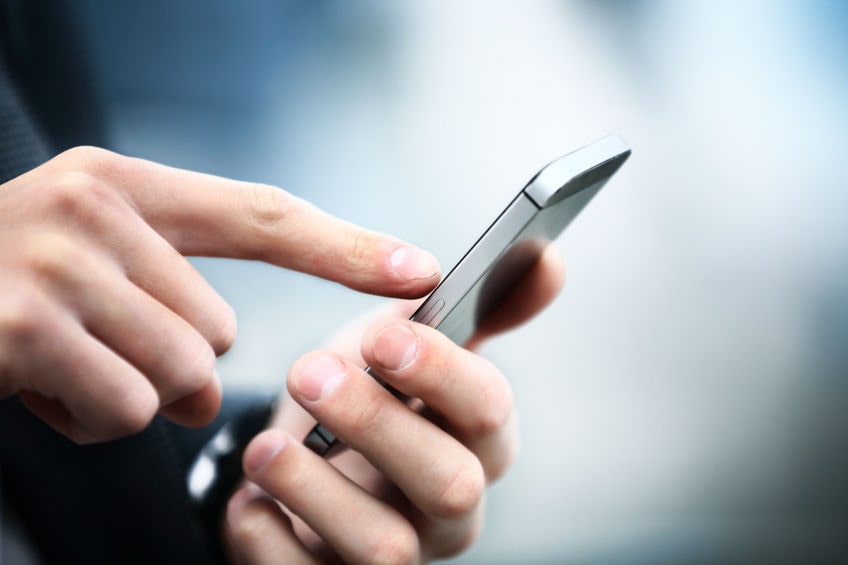
A deepfake is a video, image or audio clip that has been manipulated by AI technology to appear highly convincing. It works by overlaying an existing image or video with AI-generated content manufactured to resemble someone’s voice or appearance. Deepfakes are often referred to as a type of “synthetic media”, and their accuracy in mimicking people’s faces, voices and body movements can sometimes make it impossible to tell them apart from the real thing.
Deepfakes rely on computer systems called artificial neural networks, which are based on the human brain and are designed to recognize patterns in data. For the purposes of deepfake technology, the patterns these systems look for are rooted in biometrics like facial expressions and different pitches and tonalities of the human voice. The more data the system receives, the more accurately it can pick up on unique patterns and characteristics of a person and create a highly realistic image or video of them.
Deepfake Business Threats
The development of deepfake technology has made it increasingly difficult to discern between real and fake content, and has provided a chance for cybercriminals to exploit in their crimes. While this type of tech is still fairly new, it’s played a role in a number of fraud and cybercrime trends that businesses should be aware of. After all, the cost of a deepfake scam was projected to exceed $250 million in 2020 alone.
The risks posed by deepfake technology can vary from identity theft and automated cyberattacks to corporate fraud and extortion, and while this type of tech is still in its early stages, it’s clearly something businesses should be prepared to defend against. Here are some of the most common deepfake scams:
Ghost Fraud
Ghost fraud is when a criminal steals information from a deceased person in order to impersonate them and use their records for their own personal—and often financial—gain. Criminals might use the stolen identity to break into online accounts, pay for services they’re not authorized to, or apply for credit cards and loans.
Synthetic Identity Fraud
This type of fraud is more complex than other methods often used by criminals, and it’s usually tough to spot. Instead of going after the data and identity of a single person, criminals will mine for the data of multiple people and syndicate it to create a single “person” who doesn’t actually exist. This manufactured identity is then used in a variety of malicious ways, from large unauthorized transactions to credit applications.
New Account Fraud
New account fraud involves using either stolen or fake identities for the sole purpose of opening new bank accounts. Once a criminal manages to open a fraudulent account, they can do serious harm by maxing out credit cards or taking out loans they don’t plan to repay.
While deepfake technology certainly isn’t the first cybersecurity threat businesses have had to deal with, they represent a significant challenge that will only continue to grow as technology develops. Organizations would be wise to revisit their security strategies to ensure their data is properly secured, and make sure they have the proper security defenses in place to defend against cyber attacks.